

Customers define the quality requirements and expect on-time delivery, high performance, great service, and many more. Customers: Customers are the key to business, and they are the top priority.In addition, it provides ways to create an efficient business structure, improve the quality of the operations in an organization, and increase the bottom-line profit. Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology that uses statistical tools and techniques to define the problem and evaluate each process step. By improving processes and reducing waste, organizations can increase efficiency, reduce costs, and ultimately deliver greater value to their customers. While reducing defects is certainly an important goal in many industries, the broader focus of Six Sigma is to improve overall business performance by reducing variation and improving quality. By using statistical tools and data analysis, Six Sigma practitioners can identify the root causes of problems and develop solutions to improve process performance and meet customer needs. The core philosophy of Six Sigma is to focus on meeting or exceeding customer expectations by reducing variation and improving process performance. In addition to reducing defects, Six Sigma can also be used to improve process efficiency, reduce waste, improve customer satisfaction, and increase profitability. Is Six Sigma ONLY for Reducing Defects?Ībsolutely no! While Six Sigma is primarily known for its focus on reducing defects, it is actually a comprehensive approach to quality improvement that can be applied to a wide range of business processes. In a normally distributed process, if the mean ☓σ range of output is between USL and LSL, then around 99.73% of the points of the output will be non-defective. Let’s look at a 3 Sigma process, for example. Other Sigma Levelsįor each standard deviation away from the mean (0 in the graphic above), your process gets more and more defect-free. a 99.9999998% success rate, you have a 6 sigma process. If you only get 3.4 defects per million out of your process, i.e.

Another way to say it is that only 3.4 defects per every million products fall outside the limits we’ve set at 6 sigmas away from the center.Īdditionally, you can also think of it as a level of excellence that can be quantified and easily compared against other processes. The 6 refers to the ability to fit the good outputs of the process to fit within 6 standard deviations (or sigmas). Now let’s put them together for 6 Sigma: A Six Sigma process has a specification limit that is 6 times its sigma (standard deviation) away from its mean. The six refers to how many standard deviations away from the mean we set the specification limits in a 6 sigma process. (Also see: History of Continuous Improvement). Now, it has become a project-driven approach for process improvements that follows the five-step process, also called the DMAIC cycle. General Electric recognized benefits of $2.5 billion per year due to Six Sigma policies and made it a company-wide strategy. Later, it became a popular management approach at GE with Jack Welch in the early 1990s. While working at Motorola in the year 1986, Smith created Six Sigma as a general approach to measuring quality in business performance terms. The term Six Sigma was first coined by American engineer Bill Smith, who is known as the father of Six Sigma. wrong size, shape, or weight). To correct this, the factory uses Six Sigma to determine what’s causing the variation/defects and works to reduce them to a six-sigma level. Now, randomly sampled output discovers that out of every 1,000 widgets, fifty are flawed (e.g.
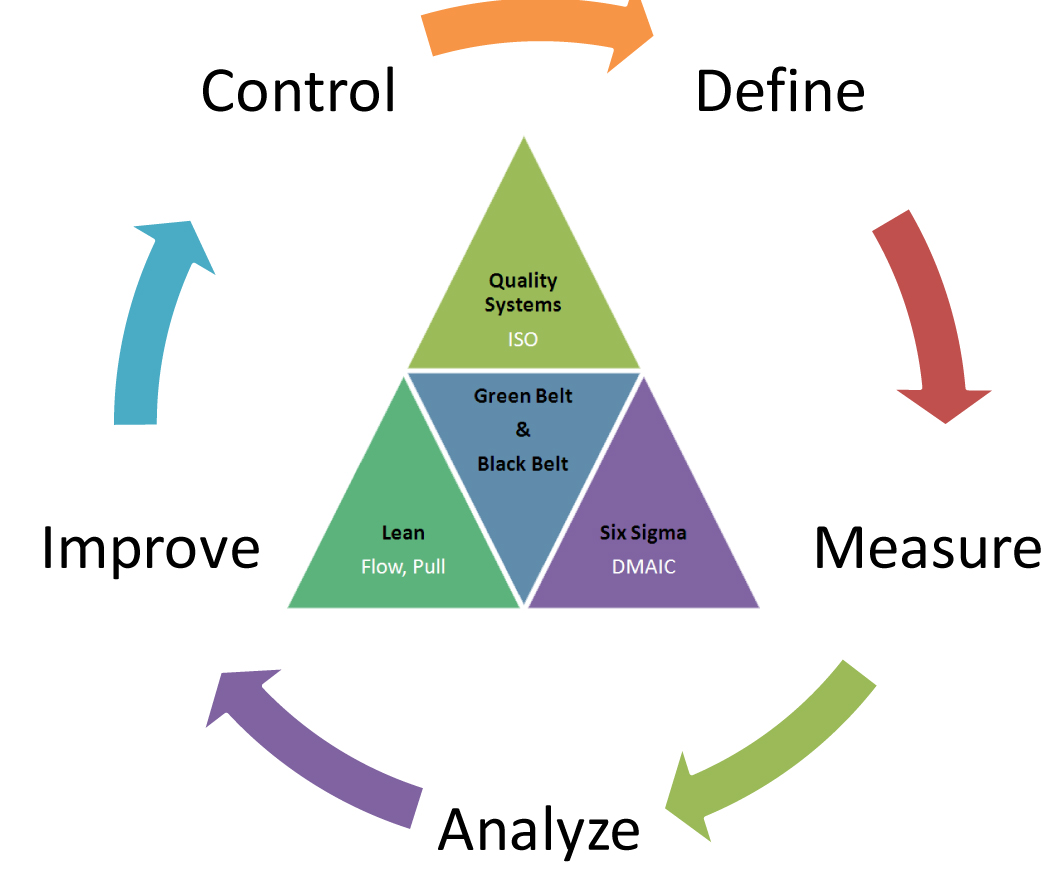
The widgets are all supposed to be a certain size, shape, and weight. Six Sigma methodologies are used to identify and remove the root cause of defects or reduce the process variation (using statistical or process analysis methods) and also the costs that are associated with it.įor example, let’s say XYZ factory produces widgets. In other words, any process performance outside of the defined specification is considered waste or a defect. Waste or defects are measurable product characteristics that do not meet the requirements of the customer (i.e. In other words, the extent to which process performance varies around the mean. Variation is the range of difference between the statistical mean and all data points that are used to calculate the mean. Hence, it focuses on variation reduction and waste elimination. The purpose of Six Sigma is to satisfy customers by producing quality products. However, it is not a standard, certification, or metric like a percentage. It is a Quality Philosophy and a management technique. Six Sigma refers to the practice of delivering products and services that perform at high standards.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
